JAVA: Operator Ternary dengan Contoh: Difference between revisions
Created page with "Operators constitute the basic building block to any programming language. Java too provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need to perform various..." |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Operator merupakan blok bangunan dasar untuk bahasa pemrograman apa pun. Java juga menyediakan banyak jenis operator yang dapat digunakan sesuai dengan kebutuhan untuk melakukan berbagai perhitungan dan fungsi, baik itu logika, aritmatika, relasional, dll. Diklasifikasikan berdasarkan fungsionalitas yang disediakan. Berikut beberapa jenisnya: | |||
Arithmetic | * Operator Arithmetic | ||
Unary | * Operator Unary | ||
Assignment Operator | * Operator Assignment | ||
Relational | * Operator Relational | ||
Logical | * Operator Logical | ||
Ternary Operator | * Operator Ternary | ||
Bitwise | * Operator Bitwise | ||
Shift | * Operator Shift | ||
Artikel ini menjelaskan semua yang perlu diketahui tentang Operator Aritmatika. | |||
==Ternary Operator== | |||
Operator ternary di Java adalah satu-satunya operator kondisional yang membutuhkan tiga operan. Ini adalah pengganti satu baris untuk pernyataan if-then-else dan banyak digunakan dalam pemrograman Java. Kita dapat menggunakan operator ternary menggantikan kondisi if-else atau bahkan mengganti kondisi menggunakan operator ternary bersarang. Meskipun mengikuti algoritma yang sama dengan pernyataan if-else, operator kondisional membutuhkan lebih sedikit ruang dan membantu menulis pernyataan if-else dengan cara sesingkat mungkin. | |||
[[File:Conditional-or-Ternary-Operator- -in-Java.jpg|center|300px|thumb]] | |||
Sintaks: | |||
variable = Expression1 ? Expression2: Expression3 | |||
Jika beroperasi mirip dengan pernyataan if-else seperti pada Exression2 dijalankan jika Expression1 true, selain itu Expression3 di jalankan. | |||
if(Expression1) | |||
{ | |||
variable = Expression2; | |||
} | |||
else | |||
{ | |||
variable = Expression3; | |||
} | |||
Contoh: | |||
num1 = 10; | |||
num2 = 20; | |||
res=(num1>num2) ? (num1+num2):(num1-num2) | |||
Since num1<num2, | |||
the second operation is performed | |||
res = num1-num2 = -10 | |||
[[File:Java-Ternary-Operator.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Flowchart of Ternary Operation]] | |||
==Example 1:== | |||
Example | |||
// Java program to find largest among two | |||
// numbers using ternary operator | |||
import java.io.*; | |||
class Ternary { | |||
public static void main(String[] args) | |||
{ | |||
// variable declaration | |||
int n1 = 5, n2 = 10, max; | |||
System.out.println("First num: " + n1); | |||
System.out.println("Second num: " + n2); | |||
// Largest among n1 and n2 | |||
max = (n1 > n2) ? n1 : n2; | |||
// Print the largest number | |||
System.out.println("Maximum is = " + max); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
Output | Output | ||
First num: 5 | First num: 5 | ||
Second num: 10 | Second num: 10 | ||
Maximum is = 10 | |||
==Example 2:== | |||
// Java code to illustrate ternary operator | |||
import java.io.*; | |||
class Ternary { | |||
public static void main(String[] args) | |||
{ | |||
// variable declaration | |||
int n1 = 5, n2 = 10, res; | |||
System.out.println("First num: " + n1); | |||
System.out.println("Second num: " + n2); | |||
// Performing ternary operation | |||
res = (n1 > n2) ? (n1 + n2) : (n1 - n2); | |||
// Print the largest number | |||
System.out.println("Result = " + res); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
Output | |||
First num: 5 | |||
Second num: 10 | |||
Result = -5 | |||
==Referensi== | ==Referensi== | ||
* https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-ternary-operator-with-examples/ | * https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-ternary-operator-with-examples/ | ||
Latest revision as of 23:26, 6 May 2022
Operator merupakan blok bangunan dasar untuk bahasa pemrograman apa pun. Java juga menyediakan banyak jenis operator yang dapat digunakan sesuai dengan kebutuhan untuk melakukan berbagai perhitungan dan fungsi, baik itu logika, aritmatika, relasional, dll. Diklasifikasikan berdasarkan fungsionalitas yang disediakan. Berikut beberapa jenisnya:
- Operator Arithmetic
- Operator Unary
- Operator Assignment
- Operator Relational
- Operator Logical
- Operator Ternary
- Operator Bitwise
- Operator Shift
Artikel ini menjelaskan semua yang perlu diketahui tentang Operator Aritmatika.
Ternary Operator
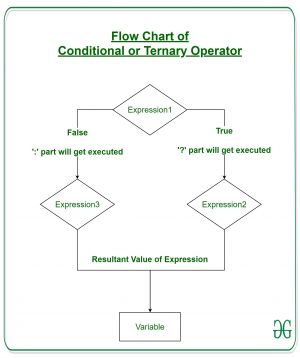
Operator ternary di Java adalah satu-satunya operator kondisional yang membutuhkan tiga operan. Ini adalah pengganti satu baris untuk pernyataan if-then-else dan banyak digunakan dalam pemrograman Java. Kita dapat menggunakan operator ternary menggantikan kondisi if-else atau bahkan mengganti kondisi menggunakan operator ternary bersarang. Meskipun mengikuti algoritma yang sama dengan pernyataan if-else, operator kondisional membutuhkan lebih sedikit ruang dan membantu menulis pernyataan if-else dengan cara sesingkat mungkin.

Sintaks:
variable = Expression1 ? Expression2: Expression3
Jika beroperasi mirip dengan pernyataan if-else seperti pada Exression2 dijalankan jika Expression1 true, selain itu Expression3 di jalankan.
if(Expression1)
{
variable = Expression2;
}
else
{
variable = Expression3;
}
Contoh:
num1 = 10; num2 = 20; res=(num1>num2) ? (num1+num2):(num1-num2)
Since num1<num2, the second operation is performed res = num1-num2 = -10
Example 1:
// Java program to find largest among two
// numbers using ternary operator
import java.io.*;
class Ternary {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// variable declaration
int n1 = 5, n2 = 10, max;
System.out.println("First num: " + n1);
System.out.println("Second num: " + n2);
// Largest among n1 and n2
max = (n1 > n2) ? n1 : n2;
// Print the largest number
System.out.println("Maximum is = " + max);
}
}
Output
First num: 5 Second num: 10 Maximum is = 10
Example 2:
// Java code to illustrate ternary operator
import java.io.*;
class Ternary {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// variable declaration
int n1 = 5, n2 = 10, res;
System.out.println("First num: " + n1);
System.out.println("Second num: " + n2);
// Performing ternary operation
res = (n1 > n2) ? (n1 + n2) : (n1 - n2);
// Print the largest number
System.out.println("Result = " + res);
}
}
Output
First num: 5 Second num: 10 Result = -5